Updated Date: Oct, 2021
About University¶
Master
- Inquiry and documents with score details Master-License
Article and Code Repository¶
Abstract1¶
Nowadays with the development of technology, we watch an increase in the number of users using cloud computing services. The process of increasing demand, the need for intelligent supply and demand cycle, better resource management, better utilization of resources is necessary. The results indicate competition from the cycle leads to a complex challenge for selecting and scheduling tasks to provide composite services in the cloud. One of the most important issues in this field is load balancing. How to choose idle resources from a set of resources, overcoming compositional constraints, determines the importance of scheduling and resource allocation. These are NP-Hard issues. State-of-the-art architecture in the field of cloud computing for the implementation of Scientific Workflows that can be implemented in a distributed manner is becoming increasingly considered in other sciences related to cloud computing. The distinction and competition of cloud service providers to publish services with more profit and better quality to customers are summarized in features such as "Scalability, Stability, High availability, Fault tolerance". By providing new solutions and services for using specialists in other sciences, we can see the utilization of cloud computing Infrastructure and services in the fields of industry, commerce, health, and emergency applications. The possibility of conducting scientific workflows using virtual machines" and containers is a goal that has been addressed in the proposed architecture. The load balancing in the form of containers at the level of virtual machines using the ant colony optimization(ACO) algorithm is one of the important goals and issues that have been covered and solutions for utilization as much as possible has been explained. According to previous studies, there is no comprehensive or stable architecture that can balance scientific workflows using the algorithm ACO at the container virtualization level. By providing a simulator environment and testing several samples with different parameters then estimated the efficiency of the ACO and default algorithm of CloudSIM e.g., first-come-first-serve (FCFS). In the case of fifty, hundred samples of "montage" scientific workflow, which is considered as the average load rate, balancing the workload of the containers on the virtual machine with the ACO has better results than the FCFS. If the value of the beta parameter of the ACO is assigned by zero, the algorithm will be trapped to the local optimal. In the case of a thousand sample, which is interpreted as a large amount of workload, if a "cybershake" workflow is used finally the results will be the same in all performance evaluation indicators. The results indicate that on average, the ACO has desired performance of almost 50% better than FCFS in the most of scenarios regarding proposed architecture and using cybershake and montage workflows.
Keywords: [[Cloud]]Computing, #ContainerAllocation, [[Workflow]], #ACO , [[Container]] Allocation, #DevOps, [[Load_Balancer]], [[Scheduler]]
Info
<iframe src="https://drive.google.com/file/d/1VIpOwOa1r9XPfNfGD7re6VazoJchVezn/preview" width="640" height="480" allow="autoplay"></iframe>
Experimental Research: CloudSim-Workflow-Function-Container-Plus (Toward ServerMix)
Pros:
- Simulation of cost and performance
- Scalability: Container is very scalable than the virtual machines
- Elasticity: with separating logical code and data
- Decrease overhead
- Decrease the start time of tasks
- Fixed data dependency
- Resource management
- Workflow Engine management
- Resource Management
Cons:
- Lack of clean code and more refactoring.
- Exclude of design patterns, modular
- Not using Maven and Unit Test
Concepts:
- Workflow: correspond with Function Composition on the simulation environment.
- Function as a Service(FaaS): Lambda or Cloud Function on the production environment.
- Cloudlet : the task of the client or job of workflow
- ACO Scheduler: Ant colony optimization
- Serverfull: include virtual machine/on-premises
- Serverless: no server, Event-driven, Provisioning, Scalability, FaaS
- ServerMix:
:
The proposed model included both of them. In implementing simulation we did not use FaaS or Lambda functions but we have some situations and marks of the Serverless as a kind of theoretical because we implemented with the capability of elasticity that is one of the Serverless features. on the other hand, we are going to need event-driven and arrow functions in this java program.
Target:
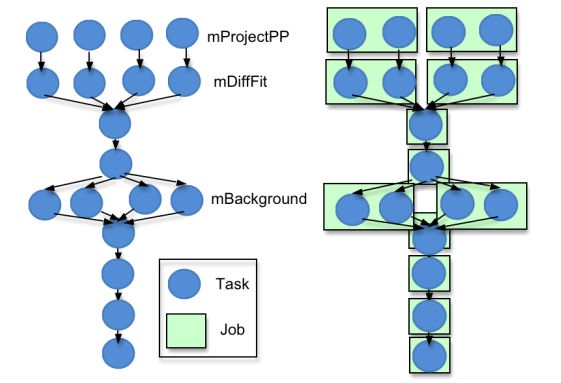
Running Montage workflow base on the container. We have two repo for implementing:
Container base on Vm: (Cloudsim-Workflow-Function-Container),(Cloudsim-Workflow-Function-Container-ACO)
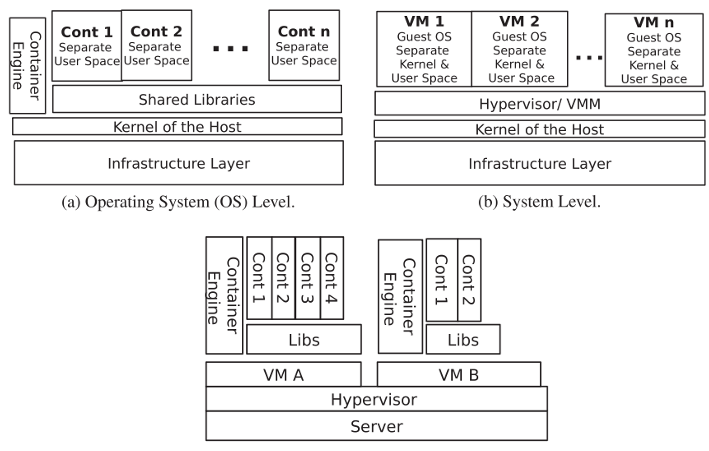 Container base on host:(CloudSim-Workflow-Function-Container-Plus), (Cloudsim-Workflow-Function-Container-ACO)
Container base on host:(CloudSim-Workflow-Function-Container-Plus), (Cloudsim-Workflow-Function-Container-ACO)
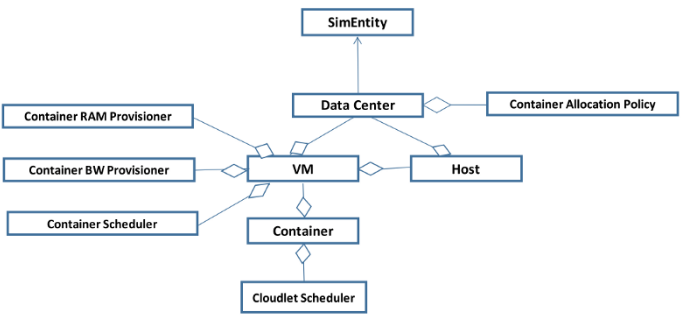 Part of class diagram: ContainerCloudsim class diagram
Part of class diagram: ContainerCloudsim class diagram
 Sequential diagram of WFC architecture:
Sequential diagram of WFC architecture:
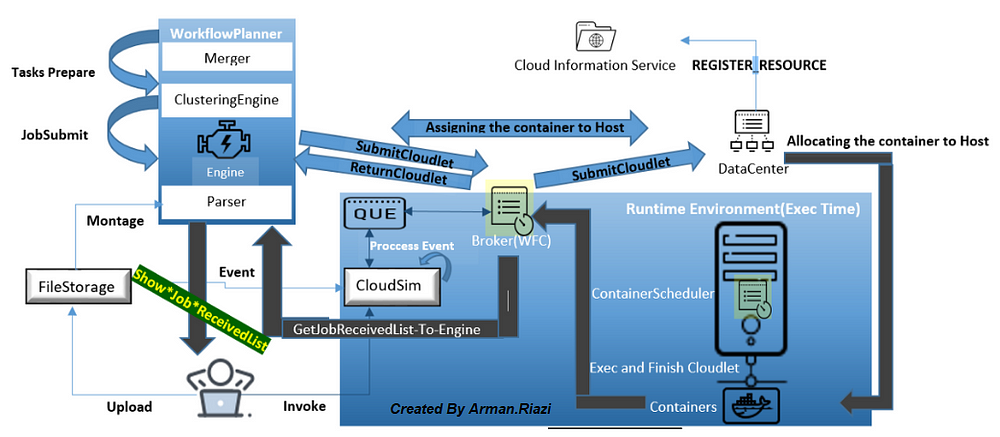 Proposed Architecture: WFC has transparency and clarity on architecture and implemented java code.
Proposed Architecture: WFC has transparency and clarity on architecture and implemented java code.
Prerequisites: Resolve project libraries include: commons-math3–3.2 | 3–6.1, flanagan, jdom-2.0.0, opencsv-2.3 (maybe) Results with montage Num.X: Season 6
Contact me: Let me know how can I help you with developing and researching. I am eager to your suggestion
References¶
[1] Malawski, M., Gajek, A., Zima, A., Balis, B., & Figiela, K. (2020). Serverless execution of scientific workflows: Experiments with hyperflow, aws lambda and google cloud functions. Future Generation Computer Systems, 110, 502-514.
[2] Kavitha, Kadarla, and S. C. Sharma. "Performance analysis of ACO‐based improved virtual machine allocation in cloud for IoT‐enabled healthcare." Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience 32, nov. 21 (2020): e5613.
[3] Leitner, Philipp, Erik Wittern, Josef Spillner, and Waldemar Hummer. "A mixed-method empirical study of Function-as-a-Service software development in industrial practice." Journal of Systems and Software 149 (2019): 340-359.
[4] Shafiei, Hossein, Ahmad Khonsari, and Payam Mousavi. "Serverless computing: A survey of opportunities, challenges and applications." arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.01296 (2019).
[5] García-López, Pedro, Marc Sánchez-Artigas, Simon Shillaker, Peter Pietzuch, David Breitgand, Gil Vernik, Pierre Sutra, Tristan Tarrant, and Ana Juan Ferrer. "Servermix: Tradeoffs and challenges of serverless data analytics." arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.11465 (2019).
[6] Pérez A, Moltó G, Caballer M, Calatrava A. Serverless computing for container-based architectures. Future Generation Computer Systems. 2018 Jun 1;83:50-9.
[7] Spillner, Josef. "Snafu: Function-as-a-service (faas) runtime design and implementation." arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.07562 (2017).
[8] Jiang, Qingye, Young Choon Lee, and Albert Y. Zomaya. "Serverless execution of scientific workflows." In International Conference on Service-Oriented Computing, pp. 706-721. Springer, Cham, 2017.
[9] Chen, Weiwei, and Ewa Deelman. "Workflowsim: A toolkit for simulating scientific workflows in distributed environments." In 2012 IEEE 8th international conference on E-science, pp. 1-8. IEEE, 2012.
[10] Piraghaj, Sareh Fotuhi, Amir Vahid Dastjerdi, Rodrigo N. Calheiros, and Rajkumar Buyya. "ContainerCloudSim: An environment for modeling and simulation of containers in cloud data centers." Software: Practice and Experience 47, no. 4 (2017): 505-521.
[11] He, Zhenxiang, Jiankang Dong, Zhengjiang Li, and Wenjuan Guo. "Research on Task Scheduling Strategy Optimization Based onACO in Cloud Computing Environment." In 2020 IEEE 5th Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC), pp. 1615-1619. IEEE, 2020.
[12] Balis, Bartosz. "HyperFlow: A model of computation, programming approach and enactment engine for complex distributed workflows." Future Generation Computer Systems 55 (2016): 147-162.
[13] Kacsuk, Peter, József Kovács, and Zoltán Farkas. "The flowbster cloud-oriented workflow system to process large scientific data sets." Journal of Grid Computing 16, no. 1 (2018): 55-83.
[14] Jonas, Eric, Johann Schleier-Smith, Vikram Sreekanti, Chia-Che Tsai, Anurag Khandelwal, Qifan Pu, Vaishaal Shankar et al. "Cloud programming simplified: A berkeley view on serverless computing." arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.03383 (2019).
[15] Wickremasinghe, B., Calheiros, R. N., & Buyya, R. (2010, April). Cloudanalyst: A cloudsim-based visual modeller for analysing cloud computing environments and applications. In 2010 24th IEEE international conference on advanced information networking and applications (pp. 446-452). IEEE.
[16] Soltani, Boubaker, Afifa Ghenai, and Nadia Zeghib. "Towards distributed containerized serverless architecture in multi cloud environment." Procedia computer science 134 (2018): 121-128.
[17] Sturm, Rick, Carol Pollard, and Julie Craig. "The NIST definition of cloud computing." In Proc. Appl. Perform. Manage.(APM) Digit. Enterprise, pp. 267-269. 2017.
[18] Karmel, Anil, Ramaswamy Chandramouli, and Michaela Iorga. Nist definition of microservices, application containers and system virtual machines. No. NIST Special Publication (SP) 800-180 (Draft). National Institute of Standards and Technology, 2016.
[19] Casalicchio, Emiliano. "Autonomic Orchestration of Containers: Problem Definition and Research Challenges." In VALUETOOLS. 2016.
[20] Cordón García, Oscar, Francisco Herrera Triguero, and Thomas Stützle. "A review on the ant colony optimization metaheuristic: Basis, models and new trends." Mathware & soft computing. 2002 Vol. 9 Núm. 2 [-3] (2002).
[21] Choe, Tae-Young. "Dynamic Task Scheduling Algorithm based on Ant Colony Scheme." (2015).
[22] Flórez, Edson, Wilfredo Gómez, and Lola Bautista. "An ant colony optimization algorithm for job shop scheduling problem." arXiv preprint arXiv:1309.5110 (2013).
[23] Katiyar, Sapna, N. Ibraheem, and Abdul Quaiyum Ansari. "Ant colony optimization: a tutorial review." In National Conference on Advances in Power and Control, pp. 99-110. 2015.
[24] Lin, Miao, Jianqing Xi, Weihua Bai, and Jiayin Wu. "Ant colony algorithm for multi-objective optimization of container-based microservice scheduling in cloud." IEEE Access 7 (2019): 83088-83100.
[25] Rani, Rama, and Ritu Garg. "Power and temperature-aware workflow scheduling considering deadline constraint in cloud." Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering 45, no. 12 (2020): 10775-10791.
[26] Gutjahr, Walter J. "ACO algorithms with guaranteed convergence to the optimal solution." Information processing letters 82, no. 3 (2002): 145-153.
-
A. Riazi [Using ACO Algorithm to Improve Performance for Container-based Scientific Workflows] - ScieNFT 2023 November NFTID: 163 ↩